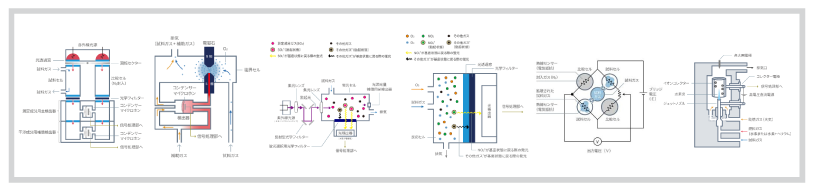
Figure 1: Basic structure of a gas analyzer using NDUV.
Ultraviolet light of a specific wavelength (incident light) from the UV light source is absorbed by O3 in the sample gas introduced into the chamber (gas cell) to be measured. How much is absorbed is obtained by measuring UV selectively transmitted through an optical filter with a photodetector. By Lambert-Beer law for the measurement of the photodetector, the concentration of O3 in the sample gas is calculated. (Figure 1)
The relationship between UV absorption and gas concentration is determined by Lambert-Beer law.
Lambert-Beer Law
The absorption amount of incident light varies corresponding to the concentration of absorbing molecules. This relationship is expressed by the Lambert-Beer law.
Ι = Ι0exp (-μcd)
Ι: Transmitted light intensity
Ι0: Incident light intensity
c: Concentration of absorbing molecules (measured component)
μ: Absorption coefficient (constant determined by molecule and wavelength)
d: Thickness of absorbing molecule layer (gas layer)